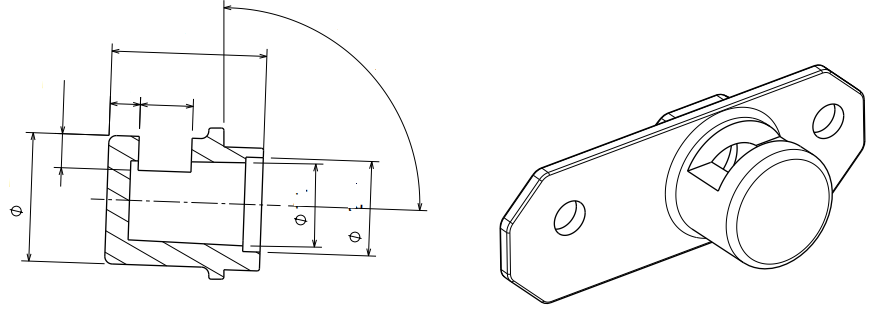
Stem inlets are critical components in various industrial applications, such as valves and piping systems, where they regulate fluid flow. Precision casting, also known as investment casting, is an ideal manufacturing method for producing stem inlets with complex geometries and tight tolerances. This guide outlines the key steps to prepare for the precision casting of a stem inlet, ensuring high performance and durability.
Step 1: Design and Engineering
- Define Functional Requirements: Determine the stem inlet’s purpose, pressure ratings, and compatibility with fluids or gases.
- Create a 3D CAD Model: Design the stem inlet with precise dimensions, including internal passages, threads, and sealing surfaces.
- Optimize for Casting: Incorporate draft angles, fillets, and machining allowances to ensure the design is castable and meets performance standards.
Step 2: Material Selection
- Choose the Right Alloy: Select a steel or stainless steel alloy that offers the necessary strength, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance (e.g., 316 stainless steel for corrosive environments).
- Verify Material Properties: Ensure the alloy is suitable for precision casting and can withstand the operating conditions of the application.
Step 3: Pattern and Mold Preparation
- Fabricate a Wax Pattern: Use injection molding or 3D printing to create a precise wax replica of the stem inlet.
- Assemble the Pattern Cluster: Attach multiple wax patterns to a central sprue to enable batch production.
- Build the Ceramic Shell: Dip the cluster into a ceramic slurry and coat it with refractory sand. Repeat the process to create a thick, heat-resistant shell.
- Cure and Dewax: Allow the ceramic shell to harden, then melt out the wax to leave a hollow cavity for casting.
Step 4: Casting Process
- Melt the Alloy: Heat the selected steel or stainless steel alloy in a furnace to the required pouring temperature.
- Pour the Molten Metal: Carefully pour the molten alloy into the preheated ceramic mold, ensuring it fills all intricate details of the stem inlet.
- Control Cooling: Allow the mold to cool gradually to minimize internal stresses and prevent defects.
Step 5: Post-Casting Operations
- Remove the Ceramic Shell: Break away the ceramic mold to reveal the raw casting.
- Cut and Separate: Detach individual stem inlets from the cluster using cutting tools.
- Clean and Finish: Remove any residual ceramic material and perform surface finishing, such as grinding or polishing, to achieve the desired surface quality.
- Inspect for Defects: Use non-destructive testing methods (e.g., X-ray or ultrasonic testing) to ensure the stem inlets are free of flaws.
Step 6: Machining and Assembly
- Machine Critical Features: Perform precision machining on sealing surfaces, threads, and other critical areas to meet tight tolerances.
- Heat Treatment (if required): Apply heat treatment to enhance the mechanical properties of the stem inlet.
- Assemble and Test: Integrate the stem inlet into the final assembly and conduct pressure tests to ensure it meets performance standards.
Conclusion
Precision casting is a highly effective method for producing stem inlets with complex geometries and exceptional performance characteristics. By following this guide, you can ensure the production of high-quality stem inlets that meet the demands of your application. Collaboration with experienced foundries and meticulous attention to detail will further enhance the success of your casting project.






